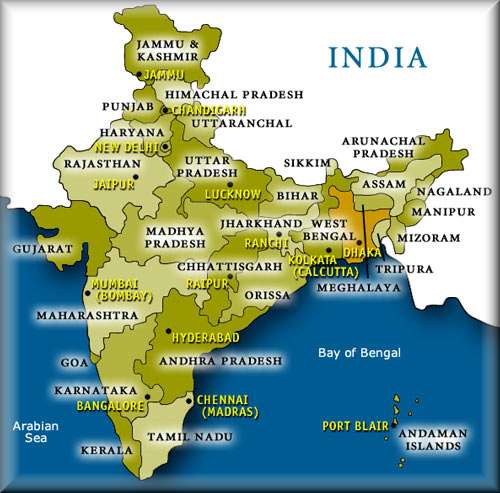
The States of India and Union Territories
The States of India and Union Territories that Make Up India
The States of India and its Union Territories make up the Country of India. In India, there are twenty-eight states and there are seven union territories that make up the Country. Similar to countries like the United States, India is divided into various states. What is different is that India also contains seven union territories, which are in addition to the States of India. So what is the difference between a state and a union territory? The difference is in the powers of a state versus a union territory. These powers are written into the Constitution of India.

Article 73 of the Constitution of India says that "the power of a Union shall extend to the matters with respect to which Parliament has power to make laws". In simple English, this means that the Federal Government of India has full say over the laws that govern all lands in India's Union Territories.
Article 162 of the Constitution of India says that "the executive power of a State shall extend to the matters with respect to which the legislature of a State has power to make laws". Meaning, again, in plain English, that the States of India are granted more independent freedom to make their own laws that govern their respective territories.
These are the twenty-eight States of India:
The Twenty-one states that are in the Country of India are Andhra Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, goa,Gujarat, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, Jharkhand,Karnataka, Kerala, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Manipur,Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Orissa, Punjab, Rajasthan, SikkimTamil Nadu, Tripura, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, and West Bengal.
These are India's seven Union Territories:
The seven Union Territories that are in the Country of India are Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Chandigarh, Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Daman and Diu, Lakshadweep, National Capital Territory and Pondicherry. The map below shows where most of these states and union territories are located. You can click on the map to visit our page with various Maps of India, or continue reading below to learn how the states were determined and divided.
The History of How the States of India and Union Territories Were Divided
You may be curious as to why the division of power between states and unions worked out this way in India. For this answer we must look at a number of factors. First, India has been ruled by many different ethnic groups throughout time. Each ruler has left a mark on the societies that they ruled and these marks can be noted throughout The history of India. Probably the most well known and documented occupational ruler of India was the British. During their rule of India, The British saw that the various regions of India were either ruled directly by the British or by local Rajas (Princes). In 1947, India gained its independence from Britain, and these land divisions were mostly preserved.

As time went on, the Indian Administrators and Parliament brought many of the princely states into the union and helped Indian people redefine themselves in these newly defined land regions. Many of the States of India became unstable because the way that the British split up India's regions did not make sense for the people of India.
As tensions rose, Parliament reorganized the country along linguistic and ethnic boundaries into states and union territories; this was known as the States Reorganization Act of 1956. The Former Portuguese and French Colonies were brought into the republic as the union territories of Puducherry and Nagar Haveli, Goa, Daman and Diu in 1962.
New territories and states have been created out of existing states as well. The Bombay State was split into the states of Gujarat and Majarashtra in 1960. Nagaland became a state in 1963, and Punjab was divided in 1966, which created the new State of Haryana. India's Northern Region was transformed into Himachal Pradesh, and Chandigarh, which was made a Union Territory.
Declarations of states were carried out for Himachal Pradesh in 1971, Manipur, Meghalaya, and Tripura in 1972, and the Kingdom of Sikhism joined in 1975. In 1987, Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram and Goa became states, but Goa's northern exclaves, Daman and Diu, became part of the Union Territories.
Recently, in the year 2000, three new states emerged. Chhattisgarh came from Eastern Pradesh, Uttarandras (Uttarakhand) was made from the hilly regions of the Northwest Uttar Pradesh, and Jharkhand came from the Southern Bikar districts. Union Territories of Dehli and Pudcherry have later been given rights to elect their own legislature and are considered some of the States of India.
Leave India States to check out popular India tourism destinations!
Check ut a physical map of India.
Visit our homepage to continue exploring India.